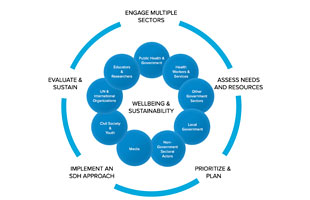
Social determinants of health

WHO strategic meeting on social determinants of health
September 2019 - Since 2018, a renewed WHO organization-wide commitment to acting on determinants of health, and therein, broader social determinants and health equity, has emerged. A new Department of Social Determinants of Health was created recently to lead this effort. This provides an opportunity to strengthen the global narrative on the social determinants of health and re-define the scope of WHO’s work in this area.
More than 50 international experts from governments and academia and over 40 WHO staff working on the determinants of health, health equity, vulnerable populations and related topics convened in Geneva for a Strategic Meeting to discuss potential priorities for the future work of WHO to address the social determinants of health.

New report shows persistent environment and health inequalities in Europe
12 June 2019 - A new WHO report launched today at the WHO High-level Conference on Health Equity in Ljubljana, Slovenia shows that intra-country inequalities in environmental exposure persist, or in some cases may have even increased. This is despite significant improvement in environmental conditions in most countries.

Healthy housing for a sustainable and equitable future – the WHO Housing and health guidelines
27 November 2018 – WHO launches the first guidelines on housing and health at the 15th International Conference on Urban Health in Kampala, Uganda. The WHO Housing and health guidelines highlight the increasing impact of housing conditions on human health in light of urban growth, climate and demographic changes. The guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations relevant to inadequate living space (crowding), low and high indoor temperatures, injury hazards in the home, and accessibility of housing for people with functional impairments. In addition, the guidelines identify and summarize existing WHO guidelines and recommendations related to housing, with respect to water quality, air quality, neighbourhood noise, asbestos, lead, tobacco smoke and radon.

Key learning on Health in All Policies Implementation from Around the World: Information brochure
23 May 2018 - WHO and Government of South Australia are delighted to have published the Progressing the Sustainable Development Goals through health in allpolicies: case studies from around the world, which describes experiences from around the world in the context of the 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda. This information brochure,distils the lessons learnt from the Case study book. It also draws on some examples of learning cited from the Global Network on Health in All Policies Meeting Report (2017).

Advanced HiAP capacity building to achieve SDGs
15 February 2018 - As part of the ongoing initiatives and programmes to provide integrated people centred health services, WHO Regional Office for Africa conducted a Health in All Policies (HiAP) workshop in South Africa’s Gauteng Province. During the workshop, the concept of HiAP was unpacked and its significance to the coordination of intersectoral action towards achieving the SDGs and addressing the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases.

Building health sector capacity to work with other sectors to achieve UHC
12 December 2017 – The newly established UHC2030 Multisectoral Action for Health Working Group will place an emphasis on building capacity for the health sector to work with other sectors as part of UHC, drawing from the Health in All Policies approach and on the political economy of multisectoral action for health, to support countries in addressing determinants of health and reaching UHC.The working group has been established by UHC2030 Steering Committee and will be co-led by the chairs, Dr Maureen Samms-Vaughan (University of the West Indies, Jamaica) and Dr Jeanette Vega (FONASA, Chile) and convened by WHO, UNICEF and World Bank.

National Health Workforce Accounts: standards on Social Determinants of Health
November 2017 – During the Fourth Global Forum on Human Resources for Health the National Health Workforce Accounts (NHWA) were launched with an aim to provide concise information on the health workforce situation and trends of a country; facilitate the standardization of a health workforce information system; as well as to support tracking Human Resources for Health policy performance towards UHC. The NHWA include three indicators related to education and training on social determinants of health and Health in All Policies approach:
- 3.05 Standards for social determinants of health [pdf, 363kb]
- 9.04 Education plans aligned with national health plan [pdf, 363kb]
- 9.01 Mechanisms to coordinate an intersectoral health workforce agenda [pdf, 363kb]
- National Health Workforce Accounts: A Handbook
- Fourth Global Forum on Human Resources Programme
- National Health Workforce Education
fact buffet
Mortality reduction in child under-5
50% was attributed to non-health sector investments by the Success Factors study (between 1990 and 2010)
Read the bulletinIntegrated social and medical services can be
10 timesmore effective than waiting for families to visit health services
Read the publicationCash transfers in Zambia increased from
62 to 84%household consumption of vitamins and resulted in less sick days reported among children and the elderly
Read the publicationWhat are social determinants of health?
The social determinants of health are mostly responsible for health inequities. Watch the video about health inequities – what are they and how do we reduce them?
Areas of work
- Health and development governance - Health in All Policies">
Health and development governance - Health in All Policies
- Health sector reorientation towards SDH">
Health sector reorientation towards SDH
- Action on key sectors for SDH">
Action on key sectors for SDH
- SDH-focused monitoring">
SDH-focused monitoring
Health in All Policies
Strategy
Resources and publications
About us
- WHO Social Determinants of Health Unit
- Strategic meeting
- World Conference on Social determinants of health
- Commission on social determinants of health